Introduction
plre
 |  |
Target: Current Landscape and Challenges
Status Quo:
In our present digital era, we have an array of modeling software available, such as Blender. However, these tools could benefit from improvements, which I propose in my idea. One primary reason is the sheer size of the files they generate. These files, often several gigabytes in size, render real-time sharing nearly impossible due to the significant database requirements and unrealistic communication conditions.
The problem amplifies when we consider current game models. Such models, based on polygons, are incredibly resource-intensive. The nature of 3D models, with their detailed structures, makes real-time sharing challenging. While typical apps and games allow pre-downloading of large data, real-time sharing in environments without pre-downloading, such as browsers, remains a challenge.
From my experience in developing realistic web-based 3D games and metaverse office services, the challenge of downloading 3D models due to data volume stands out. In my work, I often resort to advanced compression techniques when handling realistic models. Websites, constrained by storage limitations, face problems with the polygon-based approach, given the data expectations are mere MBs, which can quickly exhaust with just a single avatar's 3D model.
Projected Future:
Hypothetically, if we could represent individuals through mathematical formulas, it would allow for expression using minimal strings, solving the data volume issue. Additionally, integrating Noise into functions could generate an infinite array of model patterns. Considering creating a city's 3D map, it would inevitably require gigabytes of data. However, sharing this data in real-time remains unrealistic due to communication speeds and device capacity constraints.
As we even start to think about broader horizons, like space, interplanetary communication might become a necessity. Such long-distance communication will likely reduce communication speeds. Further, newer technological structures, like Blockchains, might not support the storage of large data volumes. Thus, even with technological advancements, the challenge of sharing large-scale data like 3D Models in real-time remains unresolved.
However, a solution emerges when considering a mathematical description-based approach to form shapes.
Traditional methods use many coordinates for basic shapes like spheres.
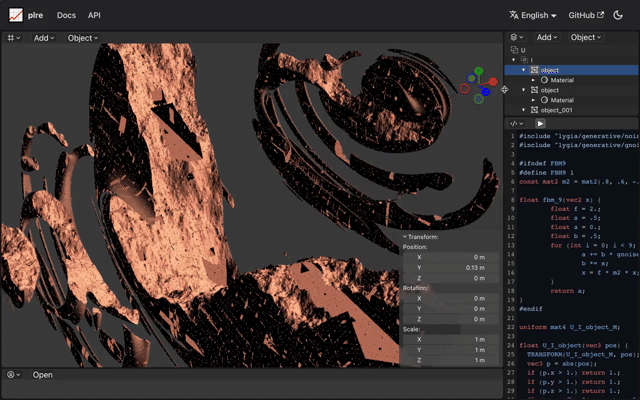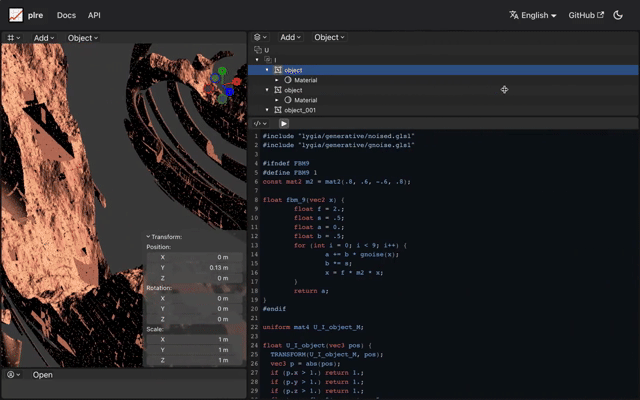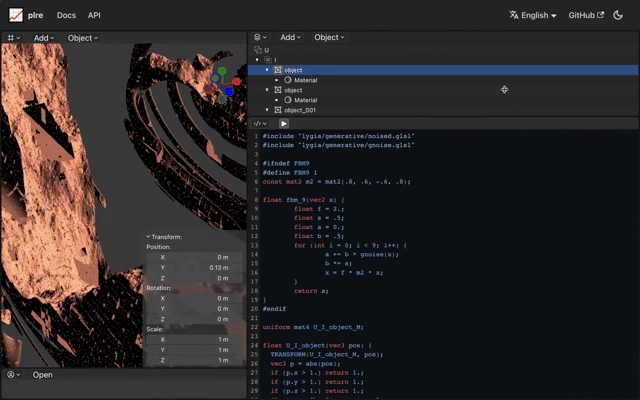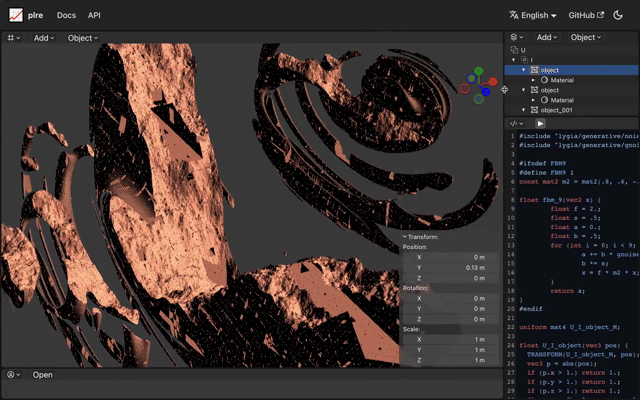
In contrast, a sphere's distance function can be as simple as length(p) - size.
Raymarch allow for the portrayal of vast landscapes using minimal code.
Present Issues:
Despite the groundbreaking potential of Raymarch, there are inherent challenges. Representing landscapes or characters using mathematical formulas demands profound knowledge in areas like GLSL, OpenGL, and more broadly, mathematics. Raymarch, despite its capability, is considered challenging and is not widely utilized beyond specific applications like visual effects or cloud representations.
Solution: A Revolutionary Approach
Conceptual Breakthrough:
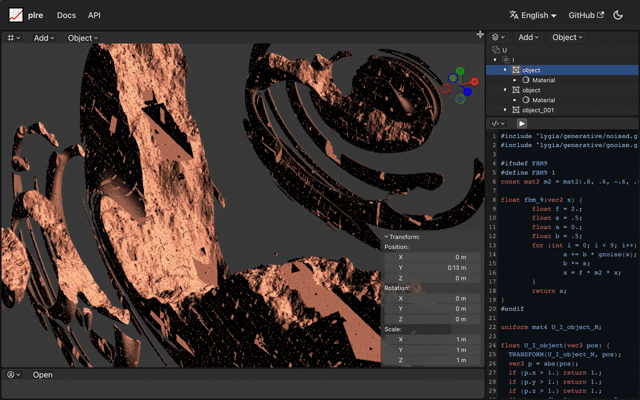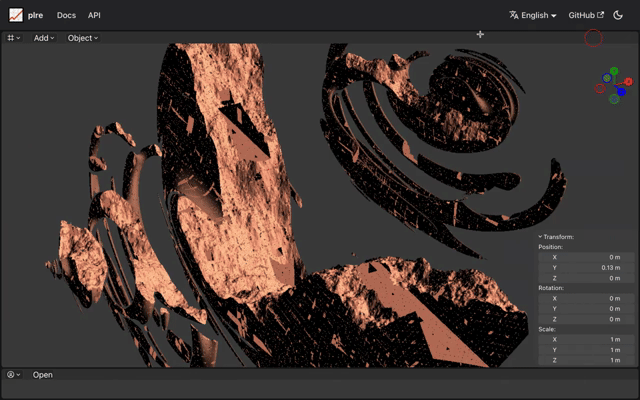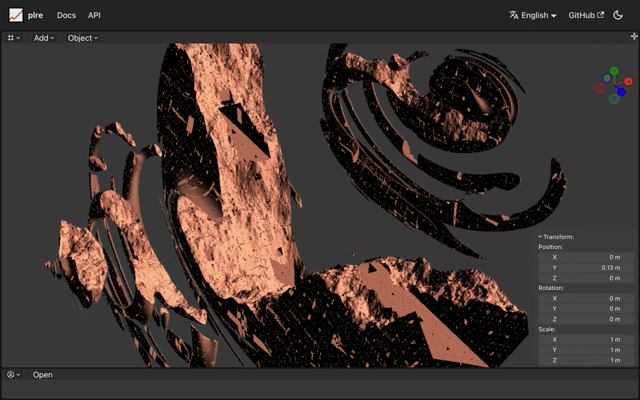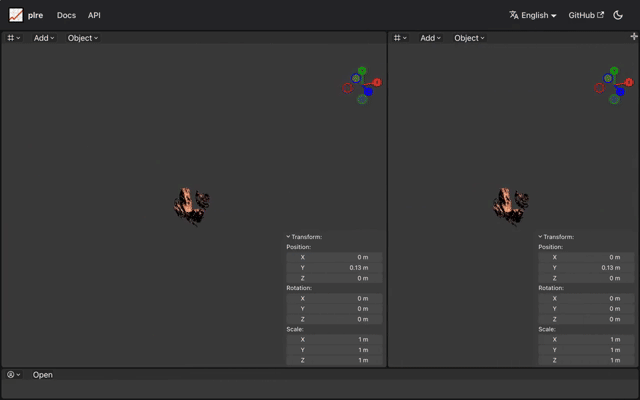
A paradigm shift emerges when we explore intuitive UI/UX designs, encapsulated in the software. Unlike traditional software that is constrained by large data files, plre opens doors to the realm of mathematical formulae. This novel approach ensures that even artists unfamiliar with linear algebra can construct 3D content seamlessly. The core idea lies in transforming the traditionally code-based representation of formulas into a structured GUI format. Furthermore, the minimalistic nature of formula-based representation enables real-time data sharing, culminating in the first-ever multi-user collaborative modeling software.
The Cascade of Benefits:
Using formulas for representation isn't just a workaround; it's an elevation in the very way we perceive modeling. Once materialized, formulas allow dynamic variations, much like having a new palette of paints that artists previously lacked. By tweaking parts of a formula or adjusting parameters, the essence of an object can be evolved far beyond its original concept. Despite the simplicity of the raymarch algorithm, it's a powerhouse that makes reproducing in varied environments feasible.
Another advantage lies in our ability to derive from the vast realm of external resources. The inclusion of shape definitions from repositories, like lygia, saves users from constantly reinventing the wheel. If the math is understood, any shape becomes feasible. This freedom extends not just to object creation but its very material. How an object interacts with light, its texture, its sheen — all can be customized to precision.
Societal Impact and The Way Forward:
The magnitude of this innovation isn't limited to its technical prowess. It's an empowerment of artists, creators, and innovators worldwide. The approach, although intricate, aims to make 3D modeling more accessible, making it accessible even to those with limited resources. The lightweight nature ensures that even in areas with bandwidth constraints, real-time collaborative 3D modeling becomes a reality.
Furthermore, the philosophy behind plre aligns with the ethos of open-source communities. By urging users to contribute unique shader designs back to the community, plre guarantees a self-sustaining, ever-evolving ecosystem. Such collaboration drives innovation, ensuring that the realm of 3D modeling continues to grow, adapt, and inspire.